|
Publication 573
J. Am.
Chem. Soc., 125 (45), 13686 -13692, 2003
DOI: 10.1021/ja0363819 S0002-7863(03)06381-9 |
|
|
Electrocatalytic Investigation of Light-Induced Electron Transfer
between Cytochrome
|
 |
Vanessa
Proux-Delrouyre, Christophe Demaille, Winfried Leibl, Pierre
Sétif, Hervé Bottin and Christian Bourdillon
Contribution from the Service de Bioénergétique,
DBJC, CEA Saclay, URA du CNRS N° 2096, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette,
France; Laboratoire d'Electrochimie Moléculaire, UMR du
CNRS N° 7591, Université Paris 7 - Denis Diderot,
75251 Paris Cedex 05, France; and Laboratoire de Technologie
Enzymatique, UMR du CNRS N° 6022, Université de Technologie
de Compiègne, B. P. 20529, 60205 Compiègne Cedex,
France. E-mail: Christian.Bourdillon@utc.fr
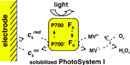
A light-activated electron-transfer chain was assembled using solubilized
cyanobacterial photosystem I as photoactive enzyme, cytochrome c6 (also
from cyanobacteria) as electron donor, and methyl viologen as electron
acceptor. The photocatalytic activity of the ensemble was measured by
direct and reversible electrochemistry of cytochrome c6 at
a surface-modified gold electrode. Analysis of the electrochemical response
with an appropriate model for the reaction mechanism allowed the relation
of the overall catalytic reaction rate to the individual steps of the
catalytic cycle. Second-order rate constants were determined for the
first time under steady-state conditions. The results validate this approach
as an efficient method for the study of electron transfer between photoactive
enzymes and their redox partners. |

