Publication
594
J.
Am. Chem. Soc. 127 (36), 12490 -12491, 2005
DOI: 10.1021/ja053911n S0002-7863(05)03911-9
|
|
|
Electrochemical Approach to Concerted Proton
and Electron Transfers-Reduction of the Water-Superoxide
Ion Complex
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cyrille Costentin, Dennis H. Evans,* Marc Robert, Jean-Michel Savéant,* and Pradyumna S. Singh
Laboratoire d'Electrochimie Moléculaire, Université de Paris 7 - Denis
Diderot, Case Courrier 7107, 2 place Jussieu, 75251 Paris Cedex 05, France, and
Department of Chemistry, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85721
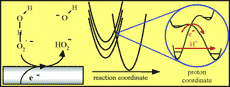
Concerted proton and electron transfers (CPET) currently attract considerable
theoretical and experimental attention, notably in view of their likely
involvement in many enzymatic reactions. Electrochemistry, through techniques
such as cyclic voltammetry, can provide a quite effective access to CPET in
terms of diagnosis and quantitative kinetic characterization. The relationships
expressing the rate constant of an electrochemical CPET are given. Besides the
CPET standard potential, it depends on two main factors. One is the
reorganization energy, which appears as the sum of an intramolecular
contribution and two solvent reorganization energies corresponding to proton and
electron transfers, respectively. The other is the pre-exponential factor that
mainly depends on proton tunneling through the activation barrier. Procedures
for estimating these various factors as well as the H/D kinetic isotope effect
are described. Application of the theory is illustrated by the experimental
results obtained for the cyclic voltammetric reduction of the water-superoxide
ion complex in dimethylformamide and acetonitrile. |

