Publication
613
J. Phys. Chem. C. , 111 , 187 - 184, 2007.
DOI:
10.1021/jp068322y
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Electrochemical concerted proton and electron tranfers. Further insights in the reduction mechanism of superoxide ion in the presence of water and other weak acids |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jean-Michel Savéant
Laboratoire d'Electrochimie Moléculaire, Université de Paris 7 - Denis
Diderot, Case Courrier 7107, 2 place Jussieu, 75251 Paris Cedex 05, France
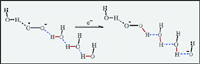
Deciphering of the role of water (or other weak acids) in the reduction of
superoxide is based on three observations: (i) very large peak potential shifts
(and hence a large increase of the apparent standard rate constant) associated
with the reaction O2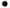 ----H2O
+ e- ----H2O
+ e- 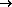 -O2H---OH- upon addition of water (or methanol,
or 2-propanol) to the acetonitrile solution; (ii) increase of the
hydrogen/deuterium isotope effect with water concentration; (iii) the fact that
the positive shift of the peak potential (or equivalently the increase of the
standard reduction rate constant) is larger with methanol than with water. Mere
invocation of specific solvation by water (or the other weak acids) of the
reduction products cannot explain these facts. They instead reveal that short
hydrogen-bonded water chains, involving approximately three water molecules, are
involved in the concerted proton-electron transfer process, thus providing a
preliminary picture of the mechanisms operating in pure water or other H-bonding
and H-bonded media.
-O2H---OH- upon addition of water (or methanol,
or 2-propanol) to the acetonitrile solution; (ii) increase of the
hydrogen/deuterium isotope effect with water concentration; (iii) the fact that
the positive shift of the peak potential (or equivalently the increase of the
standard reduction rate constant) is larger with methanol than with water. Mere
invocation of specific solvation by water (or the other weak acids) of the
reduction products cannot explain these facts. They instead reveal that short
hydrogen-bonded water chains, involving approximately three water molecules, are
involved in the concerted proton-electron transfer process, thus providing a
preliminary picture of the mechanisms operating in pure water or other H-bonding
and H-bonded media. |

