Publication
620
Biosens Bioelectron. , 22, 2906-2913, 2007.
DOI:
10.1016/j.bios.2006.12.006
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Evaluation of the analytical performances of avidin-modified carbon sensors based on a mediated horseradish peroxidase enzyme label and their application to the amperometric detection of nucleic acids |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Naîma Djellouli *, Murielle Rochelet-Dequaire*, Benoît Limoges**, Michel Druet** and Pierre Brossier *
* Laboratoire de Microbiologie Médicale et Moléculaire, Facultés de Médecine et de Pharmacie, 7 Boulevard Jeanne d'Arc, 21000 Dijon, France , and **
Laboratoire d'Electrochimie Moléculaire, UMR CNRS 7591, Université Paris 7-Denis Diderot, 2 place Jussieu, 75251 Paris Cedex 05, France
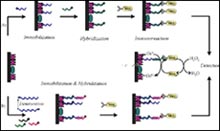
In this study, neutravidin-coated screen-printed carbon sensors were fully characterized and further used for the amperometric detection of specific DNA sequences of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV DNA). For this purpose, we took advantage of an earlier established relationship between the amount of HRP affinity immobilized on the surface of the electrode and the steady-state current recorded in the presence of H 2 O 2 as substrate and the single electron donor [Os III (bpy) 2 pyCl] 2+ as cosubstrate. After incubating a saturating concentration of biotinylated horseradish peroxidase (Bio-HRP) onto the neutravidin-modified sensors, a surface concentration of active HRP of 3.6 pmol cm -2 was calculated from the measurement of the electrocatalytic plateau current value. This result indicates that monolayers of neutravidin were adsorbed on the screen-printed carbon sensors. These neutravidin-covered platforms were then used to immobilize biotinylated nucleic acid targets. After hybridization with a complementary digoxigenin-labeled detection probe, the extent of hybrids formed was determined with an anti-digoxigenin HRP conjugate. The biosensor assay was applied to the detection of a synthetic oligonucleotide target, and then to the determination of an amplified viral DNA sequence. Monolayers of HRP-labeled oligonucleotide hybrids were immobilized onto the sensing surface whereas one third of the surface was covered with HCMV DNA hybrids. On the other hand, detection limits of 200 pM and 1 nM were obtained for the short oligonucleotide and the longer DNA targets, respectively. Finally, we demonstrated that the sensitivity of the electrochemical assay could be significantly improved by using high concentrations of the reduced form of the mediator [Os II (bpy) 2 pyCl] + , thus allowing one to detect as low as 30 pM of amplified HCMV DNA fragment. |

