Publication
624
J. Am. Chem. Soc 130, 4732-4741, 2008.
DOI:
10.1021/ja077480f
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Evidence for Concerted Pathways in Ion-Pairing Coupled
Electron Transfers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jean-Michel Savéant
Contribution from the Laboratoire d'Electrochimie Moléculaire, Unité Mixte de Recherche Université, CNRS No 7591, Université de Paris 7-Denis Diderot, 2 place Jussieu, 75251 Paris Cedex 05, France
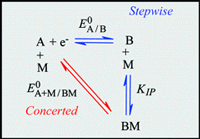
Ion-pairing with electro-inactive metal ions may change drastically the thermodynamic and kinetic
reactivity of electron transfer in chemical and biochemical processes. Besides the classical stepwise
pathways (electron-transfer first, followed by ion-pairing or vice versa), ion-pairing may also occur concertedly
with electron transfer. The latter pathway avoids high-energy intermediates but a key issue is that of the
kinetic price to pay to benefit from this thermodynamic advantage. A model is proposed leading to activation/driving force relationships characterizing such concerted associative electron transfers for intermolecular
and intramolecular homogeneous reactions and for electrochemical reactions. Contrary to previous
assertions, the driving force of the reaction (defined as the opposite of the reaction standard free energy),
as well as the intrinsic barrier, does not depend on the concentration of the ion-pairing agent, which simply
plays the role of one of the reactants. Besides solvent and intramolecular reorganization, the energy of the
bond being formed is the main component of the intrinsic barrier. Application of these considerations to
reactions reported in recent literature illustrates how concerted ion-pairing electron-transfer reactions can
be diagnosed and how competition between stepwise and concerted pathways can be analyzed. It provided
the first experimental evidence of the viability of concerted ion-pairing electron-transfer reactions. |

