Publication
703
Acc .Chem. Res., 45 (3), 228-231, 2012
DOI:10.1021/ar200132f
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Hydrogen-Bond Relays in Concerted Proton–Electron Transfers |
|
|
|
|
Julien Bonin, Cyrille Costentin, Marc Robert, Jean-Michel Savéant, and Cédric Tard
Univ Paris Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Laboratoire d'Electrochimie Moléculaire, Unité Mixte de Recherche Univ - CNRS No 7591, Bâtiment Lavoisier, 15 rue Jean de Baïf, 75205 Paris Cedex 13, France
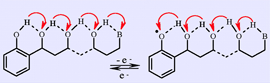
Reaction mechanisms in which electron and proton transfers are coupled are central to a huge number of processes, both natural and synthetic. Moreover, most of the new approaches to address modern energy challenges involve proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET). Recent research has focused on the possibility that the two steps are concerted, that is, concerted proton–electron transfer (CPET) reactions, rather than stepwise pathways in which proton transfer precedes (PET) or follows (EPT) electron transfer. CPET pathways have the advantage of bypassing the high-energy intermediates of stepwise pathways, although this thermodynamic benefit may have a kinetic cost. Concerted processes require short distances between the group being oxidized and the proton acceptor (and vice versa for a reduction process), which usually involves the formation of a hydrogen bond. Unlike the electron in outer-sphere electron-transfer reactions, the distance a proton may travel in a CPET is therefore rather limited. The idea has recently emerged, however, that this distance may be substantially increased via a H-bond relay located between the electron-transfer-triggered proton source and the proton acceptor. Generally speaking, the relay is a group bearing a H atom able to accept a H-bond from the moiety being oxidized and, at the same time, to form a H-bond with the proton-accepting group without going through a protonated intermediate. Although these molecules do not retain all the properties of chains of water molecules engaged in Grotthuss-type transport of a proton, the OH group in these molecules does possess a fundamental property of water molecules: namely, it is both a hydrogen-bond acceptor and a hydrogen-bond donor. Despite centuries of study, the mechanisms of proton movement in water remain active experimental and theoretical research areas, but so far with no connection to CPET reactions. In this Account, we bring together recent results concerning (i) the oxidative response of molecules containing a H-bond relay and (ii) the oxidation of phenol with water (in water) as the proton acceptor. In the first case, a nondestructive electrochemical method (cyclic voltammetry) was used to investigate the oxidation of phenol molecules containing one H-bond relay and an amine proton acceptor compared with a similar amino phenol deprived of relay. In the second, the kinetics of phenol oxidation with water (in water) as proton acceptor is contrasted with that of conventional proton acceptors (such as hydrogen phosphate and pyridine) to afford evidence of the concerted nature of Grotthuss-type proton displacement with electron transfer. First indications were provided by the same electrochemical method, whereas a more complete kinetic characterization was obtained from laser flash photolysis. Older electrochemical results concerning the reduction of superoxide ion in the presence of water are also examined. The result is a timely picture of current insight into concerted mechanisms involving electron transfer coupled with proton transport over simple H-bond relays and over H-bond networks. |

