Publication
908
Catal. Sci. Technol., 10, 4405-4411, 2020
DOI:10.1039/C9CY02552A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pH universal Ru@N-doped carbon catalyst for efficient and fast hydrogen evolution |
|
|
|
Baocheng Zheng, Li Ma, Bing Li, Dong Chen, Xueliang Li, Jianbo He, Jianhui Xie, Marc Robert, and Tai-Chu Lau
Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Advanced Catalytic Materials and Reaction Engineering, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, People's Republic of China
Université de Paris, Laboratoire d’Electrochimie Moléculaire, CNRS, F-75013 Paris, France
Department of Chemistry, City University of Hong Kong, Tat Chee, Avenue, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong, People's Republic of China
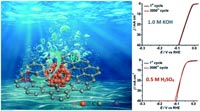
The development of efficient and cost-effective electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) is of intense interest because H2 is one of the most promising renewable energy sources. Herein, we report a highly efficient and stable HER electrocatalyst composed of ruthenium nanoparticles embedded in nitrogen-doped carbon (NC), which is synthesized via a simple thermolysis process using a ruthenium complex as metal precusor and using ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid tetrasodium (Na4EDTA) salt as ligand and carbon source. It is found that the amount of Na4EDTA employed plays an important role in achieving sutiable and uniform Ru nanoparticles. The resulting Ru@NC(1 : 5) was found to exhibit excellent HER activity and robust stability in alkaline media (1.0 M KOH) with a low overpotential at 10 mA cm-2 (29 mV), small Tafel slope (27 mV per decade) and a high turnover frequency (TOF) of 0.96 s-1 at an overpotential of 50 mV, which are comparable to the state-of-the-art commercial Pt/C catalyst. Based on the characterization of the samples and the electrochemical measurements, this high performance of Ru@NC(1 : 5) is ascribed to its smallest particle size (ca. 2.1 nm diameter), large active site density and the high electrochemical conductivity by the N-doped carbon support. In addition, Ru@NC(1 : 5) also works well in acidic media (0.5 M H2SO4) indicating it is a pH-universal catalyst. |

